The Risks and Treatment of Tooth Decay
Tooth Decay: How to Prevent and Treat This Common Dental Problem
Introduction: Tooth decay, also known as cavities or dental caries, is one of the most common dental issues worldwide. It occurs when the enamel of your teeth is damaged by acids produced by bacteria in plaque. This blog will cover the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of tooth decay to help you maintain a healthy smile.
1. What Causes Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque to build up on the teeth.
- Plaque Formation: A sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth when sugars and starches are not cleaned off.
- Acid Production: Bacteria in plaque produce acids that attack tooth enamel.
- Diet: Frequent consumption of sugary or acidic foods and drinks.
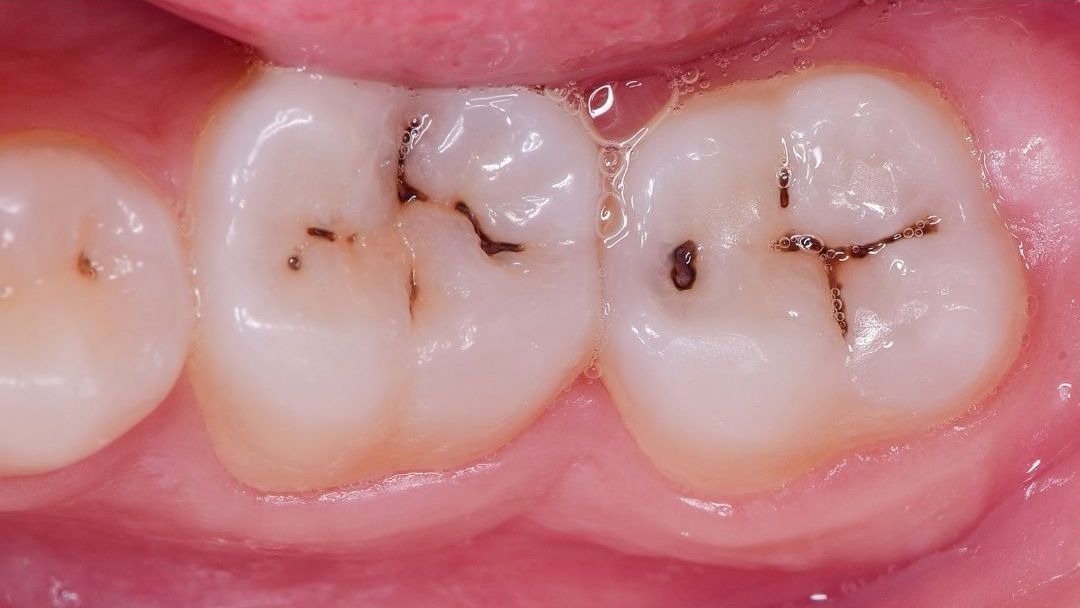
2. Symptoms of Tooth Decay
Early detection of tooth decay can prevent more serious dental problems. Common symptoms include:
- Toothache: Pain that occurs without an obvious cause.
- Sensitivity: Discomfort when eating or drinking something sweet, hot, or cold.
- Visible Holes or Pits: Cavities that can be seen on the surface of the teeth.
- Staining: Brown, black, or white stains on the teeth.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath caused by decay.
3. How to Prevent Tooth Decay
Good oral hygiene practices and regular dental visits are essential in preventing tooth decay.
- Brush and Floss Daily: Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily.
- Healthy Diet: Limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups.
- Fluoride Treatments: Use fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash, and consider professional fluoride treatments.
4. Treatment Options for Tooth Decay
The treatment for tooth decay depends on the severity of the cavities.
- Fluoride Treatments: In the early stages, fluoride treatments can help restore tooth enamel.
- Fillings: Cavities are cleaned out and filled with materials like composite resin, silver amalgam, or gold.
- Crowns: For extensive decay, a crown may be placed over the tooth.
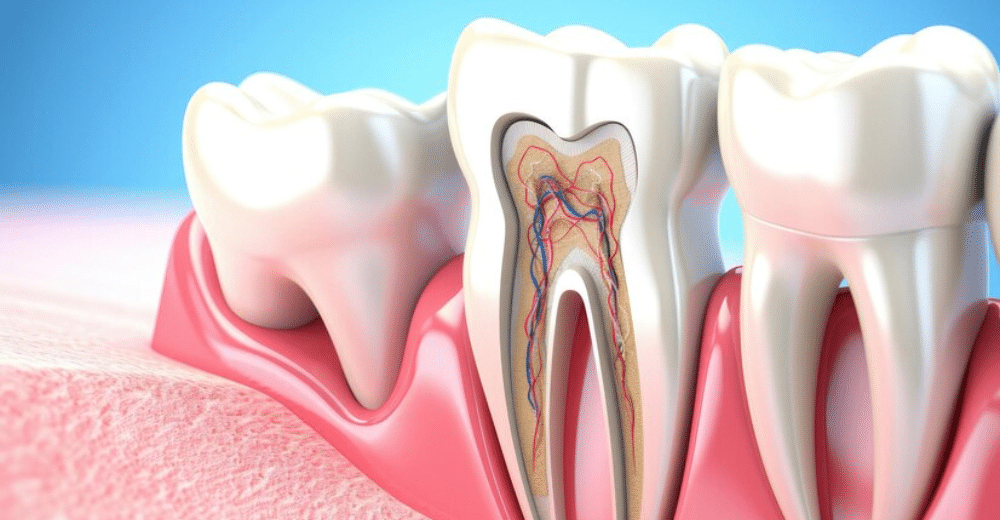
- Root Canals: If the decay reaches the tooth’s pulp, a root canal may be necessary to remove the infected tissue.
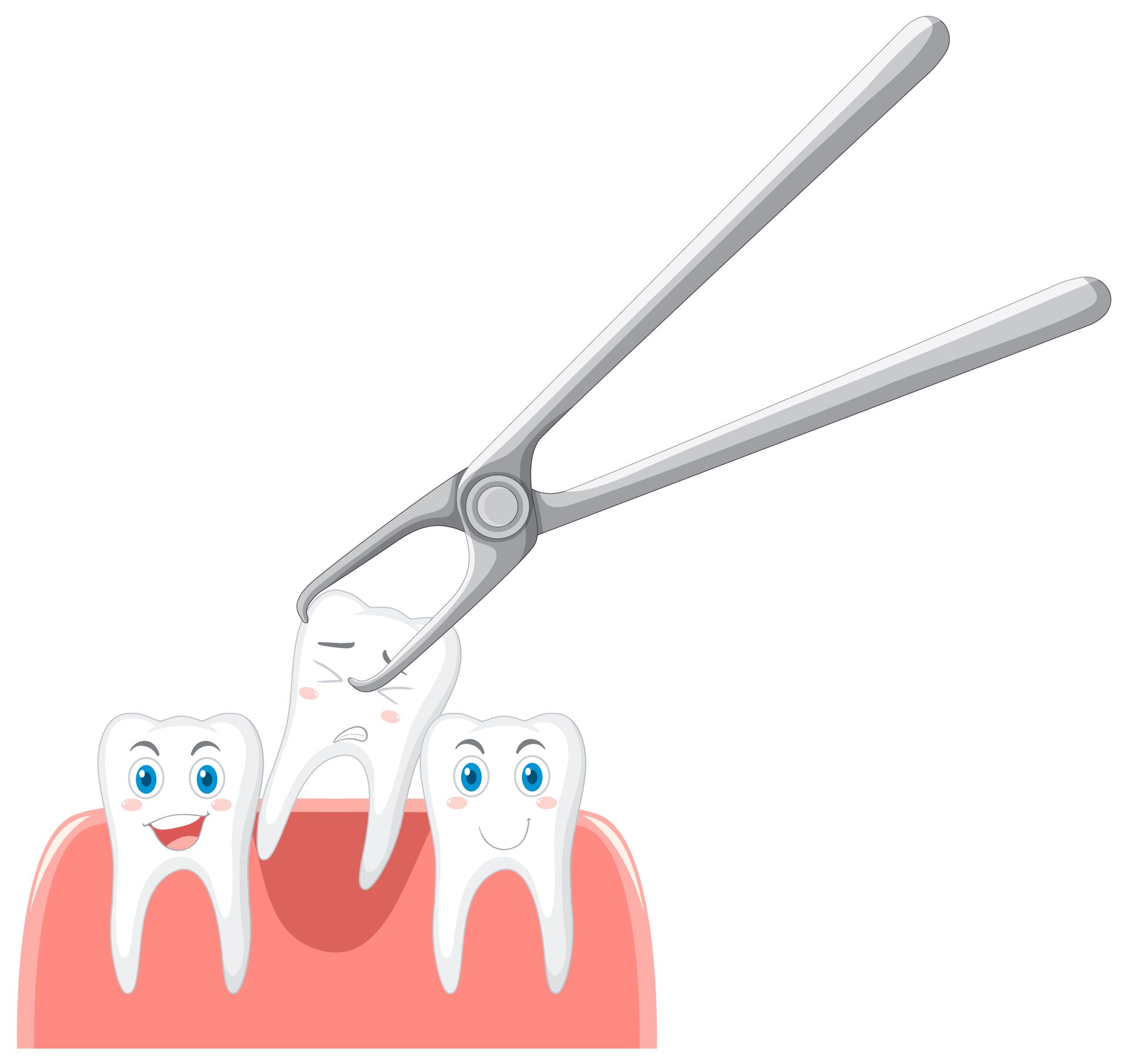
- Extractions: In severe cases, the affected tooth may need to be removed.
- Explore our Dental Treatment Options.
Conclusion: Tooth decay is a preventable and treatable condition. By maintaining good oral hygiene, making smart dietary choices, and visiting your dentist regularly, you can protect your teeth from decay and keep your smile healthy. Early detection and treatment are key to preventing more serious dental issues.